FAQs: Hair loss treatment
- What does it mean if your hair is getting thinner?
- How do I keep my hair from getting thinner?
- My dad went bald at 40 and my hair is getting thin - will I go bald too?
- At what age do men start to lose hair?
- What causes male pattern baldness?
- Can you stop male pattern baldness (androgenic/androgenetic alopecia)?
- Is male baldness reversible?
- Can women take finasteride/Propecia/minoxidil?
- Can a transgender man take finasteride?
- What is the difference between Propecia and finasteride?
- Can I take less than finasteride 1mg daily or take it less often, to reduce the risk of side effects
- How long should I take Propecia/finasteride 1mg for?
- Does Propecia/finasteride contain lactose?
- How does minoxidil work?
- Can I get Regaine (minoxidil 5%) in tablet form?
- Are there any side effects from Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
- How do I use Regaine?
- How do I use minoxidil 5% solution?
- Is the Regaine foam or solution better?
- What is 'off label' (unlicensed) use of a medicine?
- Is minoxidil 5% as effective as Regaine?
- What is the difference between Regaine and minoxidil 5%?
- Help - I started Regaine/minoxidil 5% treatment and now my hair is falling out!
- I have had chemotherapy - will Regaine/minoxidil 5% help my hair to regrow?
- I shaved my head - will Regaine/minoxidil 5% help my hair grow back more quickly?
- How long before I see a difference from using Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
- How long should I use Regaine for/minoxidil 5% for?
- Can I use minoxidil and finasteride together?
- Is there anybody who can't use Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
- Is minoxidil dangerous to children?
- How does Propecia/finasteride work?
- Are there any side effects from Propecia/finasteride?
- I have depression, can I take Propecia/finasteride?
- Is there anybody who shouldn't take Propecia/finasteride 1mg?
- My partner is pregnant/trying to get pregnant - can I use Propecia/finasteride?
- Are there any long-term side effects of taking Propecia/finasteride 1mg?
- Does finasteride or Propecia cause hair shedding?
- Can dutasteride be used to prevent hair loss in men?
- Does finasteride cause prostate cancer?
- What is female pattern hair loss?
What does it mean if your hair is getting thinner?
Thinning hair is because of a natural change to hair follicles caused by ageing and DHT (dihydrotestosterone) which comes from testosterone. The hair tends to become thinner as the follicles age and shrink. The length of time of the growing phase of a hair follicle is also reduced.
How do I keep my hair from getting thinner?
Both the anti-DHT drug Propecia, its generic equivalent finasteride, and the scalp treatment minoxidil can help to reduce hair thinning and eventual hair loss.
My dad went bald at 40 and my hair is getting thin - will I go bald too?
The tendency to develop thinning hair and balding is partly genetically determined. It can come from either of your parents. You are more likely than the general population to develop male pattern balding if a close relative already has it.
At what age do men start to lose hair?
There is no hard and fast answer, but at least half of male caucasians will have some hair loss by age 50. It can start in the 20s but more men become aware of it in their 30s and 40s. There is a genetic link, so men tend to follow a similar pattern to men in both of their parents' families.
What causes male pattern baldness?
Male pattern baldness or androgenic/androgenetic alopecia, is caused by the effect of DHT, a derivative of testosterone, on hair follicles in certain areas of the scalp. It causes shrinking of the hair follicles so reducing the hair thickness and eventually stopping the hair growth. It also reduces the length of time spent in the growing phase of the hair follicle cycle.
Further information:
Can you stop male pattern baldness (androgenic/androgenetic alopecia)?
It is not possible to stop it completely but the treatments finasteride (Propecia), and minoxidil 5% (Regaine) are very effective at reducing hair thinning. It does unfortunately continue to progress after stopping the treatments.
Is male baldness reversible?
Once baldness has developed, it is not possible to regrow the hair. Propecia/finasteride, and Regaine can help to delay total baldness by encouraging the still active hair follicles to grow thicker hair again.
Can women take finasteride/Propecia/minoxidil?
Finasteride and Propecia are not recommended for women or anyone assigned female at birth. Finasteride and Propecia can damage an unborn child in pregnancy - so women should not even handle the tablets, especially if crushed or broken.
There is a female version of Regaine which can be bought in pharmacies without a prescription (not available from Dr Fox).
Can a transgender man take finasteride?
The testosterone hormones taken to transition from female to male can also lead to male pattern hair loss and finasteride has been shown to be helpful in some of these cases. However, taking finasteride may also affect some of the other desired changes caused by the male hormones, e.g. reduction of growth of facial hair and reducing clitoral enlargement. Some trans men have also reported developing uterine bleeding or full menstrual periods when taking finasteride. Finasteride may cause harm to an unborn foetus in pregnancy and it is not licensed for use in women.
Dr Fox is unable to prescribe to transgender men, even if completely surgically transitioned and living with normal male hormone levels. If you think you may benefit from finasteride, you should discuss the benefits and risks with your usual male hormone provider.
What is the difference between Propecia and finasteride?
Both contain the same active ingredient which is finasteride. Propecia is the brand name used by the Organon pharmaceutical company for their finasteride 1mg tablets (Propecia was previously owned by Merck). Other pharmaceutical companies produce 1mg finasteride tablets, usually at lower cost, and these are known as generic Propecia.
Both branded and generic Propecia are equally effective. A lot of men have switched to generic due to cost savings and have not noticed any difference - read product reviews of finasteride 1mg.
See also generic medicines FAQs page.
Can I take less than finasteride 1mg daily or take it less often, to reduce the risk of side effects?
Many websites suggest either taking finasteride 1mg for only 3 days a week, or on alternate days, or splitting the tablets and taking either 0.25mg or 0.5mg daily, to reduce the risk of side effects from taking finasteride to treat male pattern hair loss.
Finasteride works by suppressing the conversion of testosterone to DHT (dihydrotestosterone) which causes shrinkage of hair follicles and hair loss. Research has shown that 1mg finasteride daily maintains this suppression in the majority of men. A lower dose, as in splitting the tablets, may sometimes be sufficient to suppress the effect of DHT on follicles. However, a lower than 1mg dose will not be enough for most men.
The tablets are not easy to split and may crumble, as they are film coated. It is extremely important that broken or crushed pills are not inadvertently touched by pregnant women or women who may become pregnant, as the active ingredient can be damaging to an unborn child. The film coating is an extra protection, therefore splitting finasteride pills is not recommended.
How long should I take Propecia/finasteride 1mg for?
This is an individual choice and many men take Propecia/finasteride 1mg for many years. When you do choose to stop, the beneficial effects will be lost and hair loss will restart within 6-12 months from stopping.
Does Propecia/finasteride contain lactose?
Yes. Propecia and generic finasteride tablets both contain lactose.
How does minoxidil work?
Minoxidil works by stimulating blood circulation to the scalp.
Video: How minoxidil 5% (Regaine) helps reverse hair loss
Video from Johnson & Johnson Limited.
Can I get Regaine (minoxidil 5%) in tablet form to treat hair loss?
Regaine is a topical solution or foam containing minoxidil 5% applied directly to the roots of the hair on the scalp.
Minoxidil is also available in tablet form on prescription, being licensed to treat severe high blood pressure. As a side effect from the tablets, it often also increases hair growth, both on the scalp and in all other areas of the body. The manufacturers warn of risks of salt and water retention and a rapid heart rate. These issues are probably more troublesome at the higher doses often used for blood pressure control. It is possible to buy low dose minoxidil tablets online to treat hair loss, but these are prescribed off label as there are at present (March 2024) no tablet products available with a licence to treat hair loss.
Dr Fox does not supply minoxidil tablets to treat hair loss.
Are there any side effects from Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
You may notice a temporary increase in hair loss in the first 2-6 weeks. This is entirely normal as the hair follicles are being encouraged into the growth phase. Regaine occasionally causes skin irritation that usually resolves when the treatment is stopped. Very little of the active ingredient, minoxidil, is absorbed into the circulation and therefore general side effects are not expected. For more details see Regaine Extra Strength page and the manufacturer's patient information leaflet for Regaine.
How do I use Regaine?
Use on the scalp twice daily.
- Wash your hands before using Regaine.
- Your hair and scalp should be thoroughly dry before using Regaine. Dispense a dose of 1g of foam (equivalent to the volume of half a capful) onto your fingers or apply a 1ml dose (6 sprays) of the solution with the applicator to the affected areas. There are two different applicators to choose from, with the solution, depending on how large the area to be treated is.
- Massage on to the scalp, not the hair, as it works on the hair follicles in the scalp.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after use to prevent transfer to other areas of skin.
Exceeding the recommended dose will not regrow your hair any quicker and you will have an increased likelihood of getting side effects.
For more detailed directions for use see the leaflet enclosed with the product.
How do I use minoxidil 5% solution?
Use on the scalp, twice daily.
- Wash and dry hands thoroughly before applying minoxidil 5% solution.
- Use 1ml (10 sprays from the pump spray) starting at the middle of the affected area of the scalp and massage into the scalp with fingertips. The treatment is to the scalp, not the hair itself. Do not use more than 1ml twice a day.
- Wash hands thoroughly with water after applying the solution. This is to prevent accidental application to other areas of the body, which may lead to unwanted hair growth. If any is accidentally applied elsewhere, wash that area thoroughly with lots of water.
Minoxidil 5% solution should be used long term, as hair loss will restart 3-4 months after stopping it. If there is no improvement after a year, stop the treatment.
Exceeding the recommended dose will not regrow your hair any quicker and there will be an increased likelihood of getting side effects.
For more detailed directions for use see the leaflet enclosed with the product.
Is the Regaine foam or solution better?
This is an individual choice. Both contain the same amount of active ingredient in a standard dose. The foam dries more quickly and seems to cause slightly less skin irritation as it does not contain propylene glycol. The licence for Regaine foam is for 18 years to 49 years and for Regaine solution (and generic minoxidil 5% solution) is 18 years to 65 years. In practice men up to 65 years and even beyond this age can use either one. If a medicine is used outside its licence (off-label) the manufacturer is not liable in case of adverse events. Doctors take the responsibility for the prescribing.
What is 'off-label' (unlicensed) use of a medicine?
Medicines prescribed in the UK need a licence from the MHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency). This licence lists the medical conditions that it covers. In practice many medicines can be useful for other conditions as well. The MHRA allows doctors and other specified professionals to prescribe 'off-label' (unlicensed) for other conditions. If a medicine is used for an off-label purpose the manufacturer is not liable in case of adverse events. The prescriber takes responsibility for the prescribing.
Is minoxidil 5% as effective as Regaine?
Minoxidil 5% contains exactly the same active ingredient as Regaine, which was the original marketed brand. Minoxidil 5% is equally effective as Regaine.
What is the difference between Regaine and minoxidil 5%?
Regaine is the brand name used by the original manufacturer (Johnson & Johnson) that developed and patented the treatment and initially had sole marketing rights. Minoxidil 5% is the generic form of Regaine, and is called by the actual drug name. They both contain exactly the same active ingredient - minoxidil 5% - and so work in exactly the same way.
See also generic medicine FAQs.
Help - I started Regaine/minoxidil 5% treatment and now my hair is falling out!
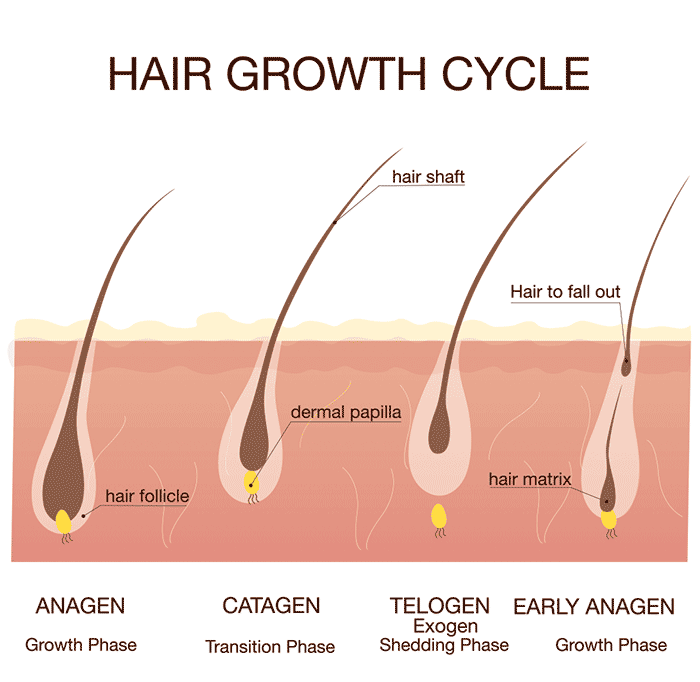
When Regaine/minoxidil 5% is first started there may be a temporary increase in hair loss for the first 2-6 weeks. This is entirely normal and is good news - it shows hair is shifting from a dormant phase into an active growing phase. It should not last longer than a few weeks, after which your hair follicles should start to grow new hairs which will eventually become thicker and stronger. For further information about the hair growth cycle see Male pattern hair loss - DermNet NZ.
I have had chemotherapy - will Regaine/minoxidil 5% help my hair to regrow?
There is no licence for use of Regaine/minoxidil 5% to encourage hair growth except in male pattern baldness. A small study in 1996, suggested that it may help after chemotherapy, but this has not been confirmed with further research.
I shaved my head - will Regaine/minoxidil 5% help my hair grow back more quickly?
Regaine/minoxidil 5% should not be used on a shaved scalp.
How long before I see a difference from using Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
Occasionally there is increased hair shedding in the first 2-6 weeks. This is a positive sign as it shows that minoxidil is stimulating the hair follicles, moving them into an active phase of hair development. New hair growth will begin after the hair has been shed. In clinical studies 90% men said that they could see change after 16 weeks when used twice a day.
See also Does finasteride or Propecia cause hair shedding?
How long should I use Regaine/minoxidil 5% for?
This is an individual choice, but when you do stop, the hair that has grown tends to disappear within 3 to 4 months and the pattern of hair loss will start again.
Can I use minoxidil and finasteride together?
Yes they work in different ways to stimulate the hair follicles and are often used together with good results.
Is there anybody who can't use Regaine/minoxidil 5%?
Regaine Extra Strength and and generic minoxidil 5% supplied by Dr Fox should NOT be used by women (a specific women's formulation is available to buy in many pharmacies). It should not be used if your hair loss is sudden or patchy; is associated with other conditions; if you have a red, inflamed, irritated, infected, or painful scalp, or there are pimples or pustules; if you have a shaved head, are wearing a dressing or bandage; or are sensitive to any of the ingredients. Discuss with your GP before using if you have heart disease or high blood pressure, even if being treated. More information in Regaine PIL. There are checks in the online hair loss assessment.
Is minoxidil dangerous to children?
If swallowed, minoxidil is very dangerous to children - it could lead to serious heart toxicity. Minoxidil, and all other medicine, MUST be kept away from children, preferably in a locked medicine cupboard.
How does Propecia/finasteride work?
In men with male pattern baldness, their hair follicles are highly sensitive to DHT. DHT speeds up the rate of hair loss by making the hair thinner until it can no longer break the surface of the scalp. Propecia/finasteride is a 5AR inhibitor which blocks enzyme that makes DHT from testosterone, so reducing the amount of DHT in the scalp. Hairs usually go through a life cycle of growth, rest, and falling out. They naturally fall out and regrow from the same hair follicle in the same place. Propecia/finasteride works at the level of hair follicles to increase the thickness of the hairs and the length of the growth phase.
Are there any side effects from Propecia/finasteride?
Most men tolerate Propecia/finasteride 1mg well and side effects are uncommon. There is an increased risk of decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or other ejaculation disorder, but this is not generally severe enough to prevent continued drug use. If drug use is stopped then these symptoms will generally resolve. However, there are some rare case reports of diminished libido or erectile dysfunction persisting after stopping the drug.
Male breast cancer is rare but has been linked to the use of all 5AR inhibitors.
Depression has been reported, and in rare cases this is linked to suicidal thoughts. If low mood, depression, or suicidal thoughts develop, stop treatment and consult your GP straight away.
I have depression, can I take Propecia/finasteride?
Depression or taking antidepressant medication does not stop you taking Propecia/finasteride 1mg tablets. However, as there have been some rare reports of men developing depression including suicidal thoughts whilst taking Propecia/finasteride, you need to be aware of this and if low mood, depression, or suicidal thoughts develop, stop treatment and consult your GP straight away.
Is there anybody who shouldn't take Propecia/finasteride 1mg?
Do not take Propecia/finasteride and consult a GP if hair loss has been rapid and recent, is patchy or irregular, or comes out in clumps, if there is scalp inflammation, or where there are also other symptoms of serious illness, such as unexplained weight loss, fevers, persistent diarrhoea, or excessive fatigue.
If you already take finasteride, or take dutasteride for an enlarged prostate, then you cannot take Propecia/finasteride 1mg for hair loss.
My partner is pregnant/trying to get pregnant - can I take Propecia/finasteride?
Pregnant women should not come into contact with finasteride. Crushed or broken tablets of Propecia/finasteride should not be handled by women when they are pregnant or are trying to get pregnant as it may affect the baby's genital organ development. Finasteride is found in semen but experts advise that, after the 1mg hair loss dose, the amount is probably too small to be significant. There are some reports of reduced fertility when taking finasteride, but fertility is reported to improve again on stopping the treatment. It is recommended to stop Propecia/finasteride for at least 2 weeks before trying to conceive.
Are there any long-term side effects of taking Propecia/finasteride 1mg?
There have been some reports of longer term issues mainly related to diminished libido or erectile dysfunction. In 2017, the NHS reviewed new research and concluded that stopping the drug would resolve sexual problems in nearly all cases. An editorial in the British Medical Journal in 2019 supported this position but suggested a need for further research. This is sometimes termed Post Finasteride Syndrome, but at present doctors don't have the research data to confirm persistent drug related problems.
Does finasteride or Propecia cause hair shedding?
Yes, finasteride and Propecia can trigger some hair shedding in the first few weeks or months. The explanation lies in the hair follicle growth cycle. Each individual hair follicle cycles between growth activity, resting, and shedding of old hair to make way for a new hair to grow. After starting to take finasteride, hair follicles which were resting, move more quickly into a growth phase. These follicles will then reach the shedding phase at a similar time, so more hair is shed. However, this is actually a good sign as it shows that the finasteride is stimulating the follicles to growth. After about 6 months, hair shedding will settle into a normal pattern and the benefits of finasteride will become more obvious.
Can dutasteride be used to prevent hair loss in men?
Dutasteride is another 5AR inhibitor which works in the same way as finasteride to prevent male pattern baldness. In theory dutasteride is more potent than finasteride, and is therefore a more effective treatment. However dutasteride does not have a licence to be used to prevent hair loss and so its prescription is off label. Dr Fox only supplies finasteride which does have a licence for the treatment of men with male pattern hair loss.
Does finasteride cause prostate cancer?
No. A Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial which ran for 10 years between 1993 and 2003 showed that 25% fewer men developed prostate cancer if taking finasteride. However, that study also seemed to show that the prostate cancers which were found were more aggressive. However more recent re-analysis of the results and other more recent studies have been done. These confirm that there are 25-30% fewer men developing prostate cancer if taking finasteride. The mortality (death rate) from prostate cancer in men taking and not taking finasteride is about the same. It now appears that the original finding of more aggressive cancers was likely due to better cancer detection during the trial.
What is female pattern hair loss?
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is also usually due to genetic inheritance and results in diffuse hair loss. Approximately 40% of women are affected by age 50, 55% by age 80. However it is not usually linked to testosterone. Many women who have raised testosterone levels do not experience hair loss so the treatments used for male pattern hair loss will not be helpful. It is recommended that if you have concerns over hair loss that you review this with your usual GP as they may arrange further tests to see if there is another underlying cause. There are treatments available over the counter, such as Regaine for women and the NHS have a good resource on how to cope with this. We do not supply treatment for female hair loss at Dr Fox.
Hair loss treatment
Authored 01 December 2020 by Dr A. Wood
MB ChB Manchester University 1984. Former NHS GP in Bristol. GMC no. 2855422
Reviewed by Dr C. Pugh, Dr B. Babor
Last reviewed 06 March 2024
Last updated 17 October 2025
Editorial policy


